Key Takeaways
ISO 9001's design and development processes are detailed in sections 8.3 and 8.4 of the standard.
Clear documentation, defined roles, and stakeholder involvement are crucial for compliance.
Regular audits and reviews ensure continuous improvement and adherence to standards.
Effective risk management is essential for identifying, evaluating, and mitigating potential risks.
Feedback from stakeholders helps refine processes and enhance product quality.
ISO 9001 Design & Development Process Tips & Best Practices
Why Effective Design & Development Matter
Effective design and development processes are the backbone of any organization aiming for ISO 9001 certification. These processes ensure that products and services meet customer expectations and comply with regulatory requirements. Most importantly, they help reduce risks, improve efficiency, and drive innovation.
Think about it: a well-structured design and development process not only boosts product quality but also enhances customer satisfaction. When customers are happy, they are more likely to return and recommend your products to others.
Understanding ISO 9001 Requirements
Key Sections: 8.3 and 8.4
ISO 9001 outlines specific requirements for the design and development of products and services. Sections 8.3 and 8.4 are particularly important as they detail the criteria, processes, and evaluations necessary for compliance. See our Design and Development online Course

Section 8.3 focuses on the design and development of products and services. It emphasizes the need for a structured approach, including planning, inputs, controls, and outputs. For more details, you can read about ISO 9001:2015 Clause 8.3. Section 8.4, on the other hand, deals with the control of externally provided processes, products, and services. This section ensures that any external contributions meet the organization's quality requirements. See also 8.1 as it provides broad requirements for operational planning and control.
Compliance Criteria and Processes
To comply with ISO 9001, organizations must establish clear criteria and processes for their design and development activities. This includes defining the necessary steps, identifying required resources, and setting up controls to monitor progress.
Here are some key steps to ensure compliance:
Define the scope of the design and development activities.
Identify the necessary inputs, such as customer requirements and regulatory standards.
Establish controls to monitor and verify each stage of the process.
Document the outputs, including specifications, drawings, and test results.
Evaluation and Verification Steps
Evaluation and verification are critical components of the design and development process. They ensure that the outputs meet the specified requirements and that any issues are identified and addressed promptly.
To effectively evaluate and verify your design and development activities, consider the following steps:
Conduct regular reviews at key stages of the process. These are preset as defined in the procedure. Exceptions can be made if justified in the planning document.
Perform testing and validation to confirm that the outputs meet the requirements.
Document the results of evaluations and verifications.
Implement corrective actions if any discrepancies are found.
Setting Up the Design and Development Process
Defining Clear Steps and Milestones
Establishing a clear and structured design and development process is essential for achieving ISO 9001 compliance. This involves defining specific steps and milestones to guide the process from start to finish.
Here’s a simple way to break it down:
Initiation: Define the project scope, objectives, and deliverables.
Planning: Develop a detailed plan outlining the required resources, timelines, and responsibilities. Ensure to address all from a-j in the Standard.
Execution: Carry out the design and development activities according to the plan. Includes for verification and validation for each phase.
Monitoring: Regularly review progress and make adjustments as needed.
Closure: Finalize the project, document the results, and conduct a post-project review.
Change Mgmt: A good formal engineering change process.

Documenting Requirements and Outputs
Documentation and record keeping are the cornerstones of the ISO 9001 design and development process(and found to be the weakest). It provides a clear record of requirements, activities, and outcomes, ensuring transparency and accountability. Highly suggest to ensure by the dates of each Design Review ensure for proper organization of documents and records in the electronic file structure as if an auditor would be viewing such files.
When documenting requirements and outputs, keep the following tips in mind:
Clearly define the company, customer and regulatory requirements.
Document the design and development activities, including any changes and their rationale.
Maintain records of evaluations, verifications, validation and test results.
Ensure that all documentation is easily accessible and well-organized in a consistent file structure.
Roles and Responsibilities
Assigning clear roles and responsibilities is crucial for the success of the design and development process. This ensures that everyone involved understands their tasks and can contribute effectively to the project. For more information, you can read about the ISO 9001:2015 design and development process.
Consider the following roles:
Project Manager: Oversees the entire process and ensures that it stays on track.
Design Engineer(s): Responsible for creating the design and ensuring it meets the requirements.
Quality Assurance: Monitors the process to ensure compliance with ISO 9001 standards.
Stakeholders: Provide input and feedback throughout the process.
Effective Planning and Risk Assessment
Effective planning and risk assessment are essential for a successful design and development process. By identifying potential risks early on, you can develop strategies to mitigate them and ensure that the project stays on track.
Here are some steps to help with planning and risk assessment:
Identify potential risks and their impact on the project.
Evaluate the likelihood of each risk occurring.
Develop mitigation plans to address the identified risks.
Continuously monitor and update the risk assessment throughout the project.
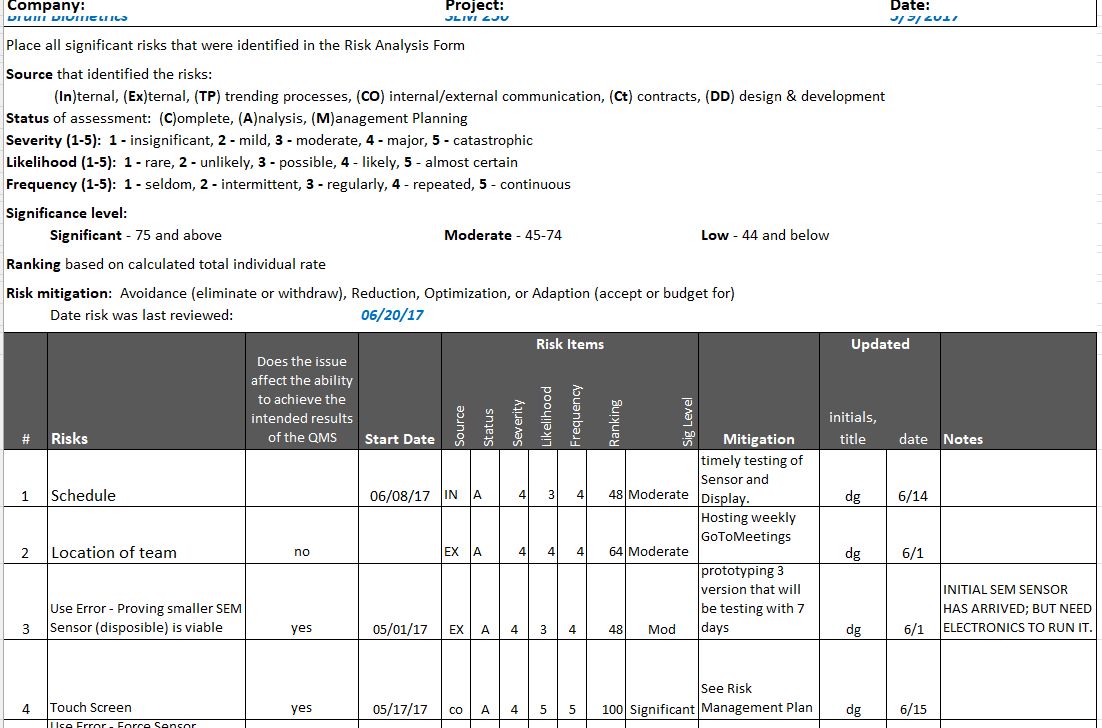
Best Practices for Implementation
Implementing ISO 9001 design and development processes can be challenging, but following best practices can simplify the task. These practices ensure that the processes are effective, efficient, and compliant with the standard's requirements. The challenge is to ensure consistency across all engineers.
First, start with comprehensive documentation. Documenting every step of the design and development process provides a clear record of activities and decisions. This transparency is crucial for audits and continuous improvement.
Comprehensive Documentation
Effective documentation involves more than just keeping records. It means creating detailed, clear, and accessible documents that everyone involved in the process can understand and use.
Document the design and development plan, including objectives, scope, and timelines.
Maintain records of design inputs, such as customer requirements and regulatory standards.
Keep detailed logs of design reviews, changes, and approvals.
Ensure that all documents are stored in a central, easily accessible location.
Stakeholder Involvement
Involving stakeholders in the design and development process is essential for success. Stakeholders provide valuable insights, feedback, and support that can help improve the quality of the final product.
Here are some ways to involve stakeholders effectively:
Identify all relevant stakeholders, including customers, suppliers, and internal teams.
Engage stakeholders early in the process to gather their requirements and expectations.
Hold regular meetings to update stakeholders on progress and gather feedback.
Incorporate stakeholder feedback into the design and development process.
Communication and Collaboration
Good communication and collaboration are vital for a successful design and development process. They ensure that everyone involved is on the same page and can work together effectively.
Consider these tips to improve communication and collaboration:
Establish clear communication channels and protocols.
Use collaborative tools and platforms to share information and documents.
Encourage open and honest communication among team members.
Hold regular team meetings to discuss progress, challenges, and next steps.
Integrating Risk Management
Risk management is a critical component of the ISO 9001 design and development process. By identifying and addressing potential risks early, you can prevent issues that could derail the project and ensure that the final product meets quality standards. For more information, check out this design and development plan for ISO 9001.
Identifying Potential Risks
Start by identifying all potential risks that could impact the design and development process. These risks could be related to technical challenges, resource constraints, or external factors such as regulatory changes.
To identify risks, consider the following:
Conduct brainstorming sessions with the project team and stakeholders.
Review past projects to identify common risks and issues.
Analyze industry trends and regulatory changes that could impact the project.
Evaluating Impact and Likelihood
Once you have identified potential risks, evaluate their impact and likelihood. This helps prioritize risks and focus on those that pose the greatest threat to the project.
Consider these factors when evaluating risks: internal audit programs, market conditions, and regulatory changes.
Impact: How severe would the consequences be if the risk materializes?
Likelihood: How likely is it that the risk will occur?
Detectability: How easily can the risk be detected before it causes significant issues?
Creating Mitigation Plans
For each identified risk, develop a mitigation plan to address it. These plans should outline the steps to take if the risk occurs and assign responsibilities for managing the risk.
Effective mitigation plans include:
Specific actions to reduce the likelihood or impact of the risk.
Clear roles and responsibilities for implementing the actions.
Timelines for completing the actions.
Contingency plans for managing the risk if it occurs.
Continuously Monitoring Risks
Risk management is an ongoing process. Continuously monitor risks throughout the design and development process to ensure that new risks are identified and existing risks are managed effectively.
To monitor risks effectively:
Regularly review and update the risk assessment.
Track the progress of mitigation actions and adjust them as needed.
Conduct periodic risk reviews with the project team and stakeholders.
Document any changes to the risk assessment and mitigation plans.
Conducting Audits and Reviews
Audits and reviews are essential for ensuring that the design and development process complies with ISO 9001 standards and identifying areas for improvement. Regular audits provide objective evidence of compliance and help maintain the effectiveness of the process.
Setting Up Regular Audits
Establish a schedule for regular audits to review the design and development process. These audits should be conducted by qualified personnel who are independent of the process being audited. For more insights, consider how to transform your internal audit program to drive organizational success.
When setting up audits, consider the following:
Define the scope and objectives of each audit.
Select qualified auditors with relevant expertise.
Develop an audit plan that outlines the audit process and timelines.
Ensure that audit findings are documented and communicated to relevant stakeholders.
Reviewing Compliance and Effectiveness
During audits, review the design and development process to ensure compliance with ISO 9001 requirements and assess its effectiveness. This involves examining documentation, interviewing personnel, and observing activities.
Key areas to review include:
Compliance with documented procedures and standards.
Effectiveness of design controls and verification activities.
Accuracy and completeness of documentation.
Implementation of corrective actions for identified issues.
Addressing Areas for Improvement
After the audit, address any areas for improvement identified during the review. This involves developing and implementing corrective actions to resolve issues and prevent their recurrence.
To address areas for improvement, you can learn more about the ISO 9001:2015 design and development process.
Develop a corrective action plan that outlines the steps to be taken.
Assign responsibilities for implementing the corrective actions.
Set timelines for completing the corrective actions.
Monitor the effectiveness of the corrective actions and make adjustments as needed.
Feedback and Continuous Improvement
Feedback and continuous improvement are essential components of a robust ISO 9001 design and development process. By actively seeking feedback and implementing changes based on that feedback, organizations can enhance their processes and products, ensuring they meet customer expectations and regulatory requirements.
Continuous improvement is not a one-time effort but an ongoing commitment to excellence. It involves regularly evaluating processes, identifying areas for improvement, and making necessary adjustments to achieve better results.
Collecting Stakeholder Feedback
Collecting feedback from stakeholders is crucial for continuous improvement. Stakeholders, including customers, suppliers, and internal teams, provide valuable insights that can help identify areas for enhancement.
Conduct surveys and interviews to gather feedback from customers and suppliers.
Hold regular meetings with internal teams to discuss process performance and potential improvements.
Encourage open communication and create channels for stakeholders to provide feedback easily.
Analyze feedback data to identify common themes and areas for improvement.
Implementing Improvements Based on Feedback
Once feedback is collected, it's essential to implement improvements based on that feedback. This involves analyzing the feedback, identifying actionable items, and making necessary changes to processes and practices. For more insights, consider exploring integrated process management strategies.
For example, if customers consistently report issues with a particular product feature, the design team should investigate the issue, identify the root cause, and implement changes to address it. This could involve redesigning the feature, improving quality control, or providing additional training to employees.
Updating Processes and Best Practices
Updating processes and best practices based on feedback and continuous improvement efforts is crucial for maintaining ISO 9001 compliance and ensuring ongoing success. This involves regularly reviewing and revising documented procedures, training materials, and quality management practices.
Organizations should establish a process for regularly reviewing and updating their design and development processes. This could involve conducting periodic process reviews, benchmarking against industry standards, and incorporating new technologies and methodologies. For more information, you can refer to this guide on understanding ISO 9001:2015 Clause 8.3.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
Implementing and maintaining an effective ISO 9001 design and development process requires a structured approach, clear documentation, and a commitment to continuous improvement. By following the tips and best practices outlined in this article, organizations can ensure compliance with ISO 9001 standards, enhance product quality, and improve customer satisfaction. For more insights, check out our guide on aligning design and development procedures with company culture.
Remember, the key to success lies in understanding the requirements, involving stakeholders, managing risks, and continuously seeking feedback and making improvements. With dedication and attention to detail, any organization can achieve and maintain ISO 9001 certification, driving innovation and excellence in their design and development processes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the significance of ISO 9001 in design and development?
ISO 9001 provides a framework for organizations to ensure that their design and development processes meet customer requirements and regulatory standards. It emphasizes a structured approach, clear documentation, and continuous improvement, helping organizations enhance product quality and customer satisfaction. For more insights, you can read about the ISO 9001:2015 Clause 8.3.
How do I ensure compliance with ISO 9001?
To ensure compliance with ISO 9001, organizations should establish clear criteria and processes for their design and development activities. This includes defining the necessary steps, identifying required resources, setting up controls to monitor progress, and conducting regular audits and reviews to assess compliance and effectiveness.
What are common challenges in implementing ISO 9001?
Common challenges in implementing ISO 9001 include understanding the standard's requirements, ensuring comprehensive documentation, involving stakeholders, managing risks, and maintaining a commitment to continuous improvement. Overcoming these challenges requires a structured approach, clear communication, and ongoing training and support. For more insights, you can read about planning for ISO 9001 implementation.
How often should I conduct audits?
Organizations should conduct regular audits to ensure compliance with ISO 9001 standards and identify areas for improvement. The frequency of audits can vary depending on the complexity of the design and development process, but it's generally recommended to conduct audits at least annually or more frequently if significant changes occur. Design process should be considered a critical process and to be audited more frequently than other processes.
Regular audits provide objective evidence of compliance and help maintain the effectiveness of the design and development process.” – ISO 9001 Standard
What are the benefits of stakeholder involvement in the process?
Involving stakeholders in the design and development process provides valuable insights, feedback, and support that can help improve the quality of the final product. Stakeholders, including customers, suppliers, and internal teams, can identify potential issues, provide input on requirements and expectations, and contribute to continuous improvement efforts.

